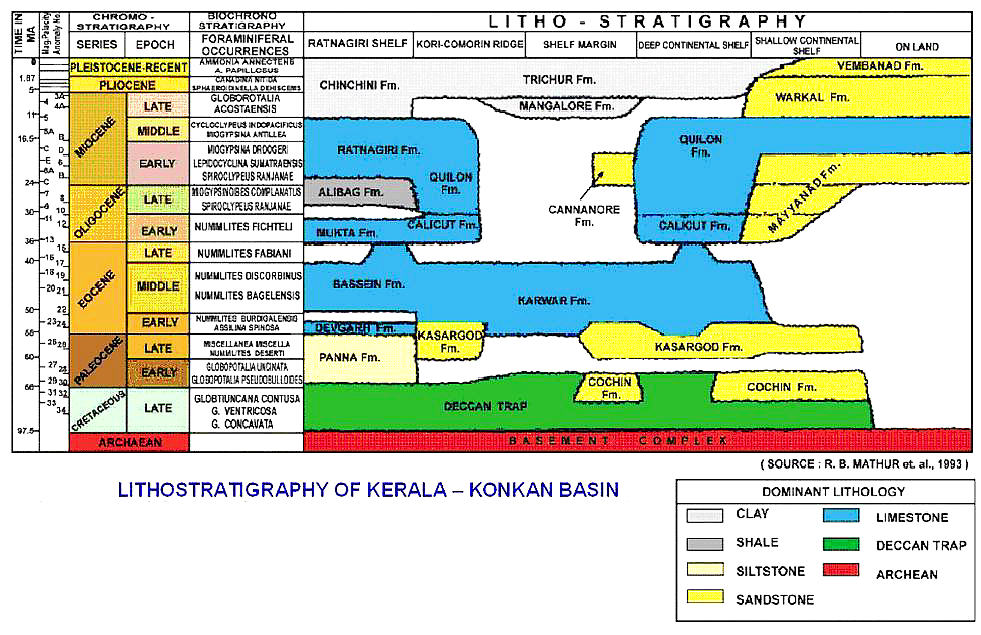
Warkali Fm
Type Locality and Naming
OUTCROP: Outcrop near Warkali. [Original Publication: King, W., 1882: The Warkali beds and associated deposits at Quilon in Travancore, Rec. Geol. Surv. Ind. Vol. 15 (2). pp. 93-102]. Reference section: Ambalapuzha, Interval between 620-220m and thickness is 400 m.
Synonyms: This sequence was called Warkhali Beds by King (1882). The name Ambalapuzha Fm was given by Raha and Rajendran, (1984). Subsequently Zushi et al., (1985) have maintained Warkali Fm giving preference to the established nomenclature.
Lithology and Thickness
Coarse-grained sandstone. Pebbly coarse sand, variegated and mottled clays and peat / Lignite in the onshore area. Alternation of sand sticky carbonaceous clay with lignite band and coarse pebbly sand occur near the base of the formation. Its thickness is 400 m in reference section.
[Figure 1: Lithostratigraphy of Kerala-Konkan Basin (from dghindia.gov.in)]
Relationships and Distribution
Lower contact
Lower boundary is unconformably overlies Quilon Fm
Upper contact
Upper boundary is unconformably with Vembanad Fm.
Regional extent
GeoJSON
Fossils
Kern et al., 2013 reported mangrove flora composed of Rhizophoraceae, Avicennia, Xylocarpus and Sonneratia from Warkali cliff section. Despite close similarity between Miocene and modern vegetation, they observed abundance of Nypa and absence of gymnosperms in the Miocene vegetation. They concluded that the paleo-vegetation of Early and Middle Miocene of southern India appears to be more uniform than today.
Age
Depositional setting
Marginal marine
Additional Information